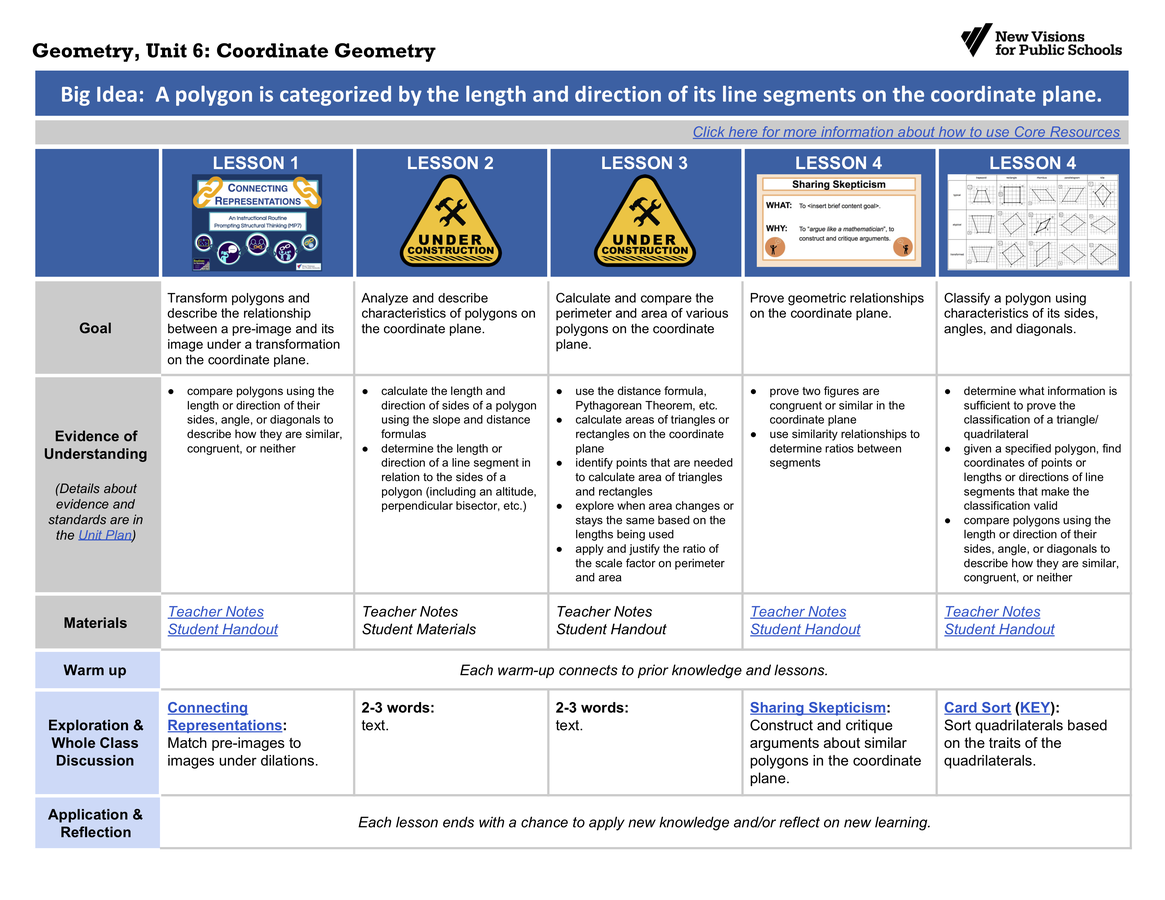
Evidence of Understanding
- analyze and describe characteristics of polygons on the coordinate plane
- calculate the length and direction of sides of a polygon using the slope and distance formulas
- determine the length or direction of a line segment in relation to the sides of a polygon (including an altitude, perpendicular bisector, etc.)
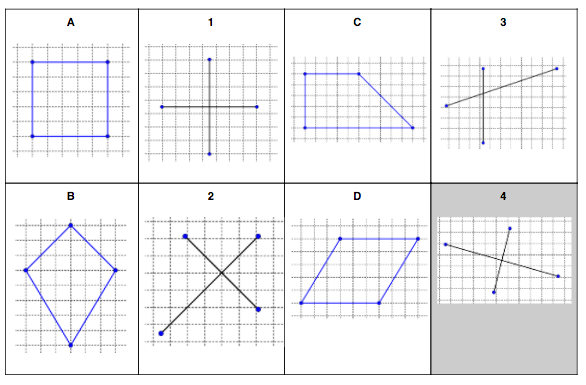
- compare polygons using the length or direction of their sides, angle, or diagonals to describe how they are similar, congruent, or neither
- calculate and compare the perimeter of various polygons on the coordinate plane
- use the distance formula, Pythagorean Theorem, etc.
- calculate areas of triangles or rectangles on the coordinate plane
- identify points that are needed to calculate area of triangles and rectangles
- explore when area changes or stays the same based on the lengths being used (Example: height of a triangle)
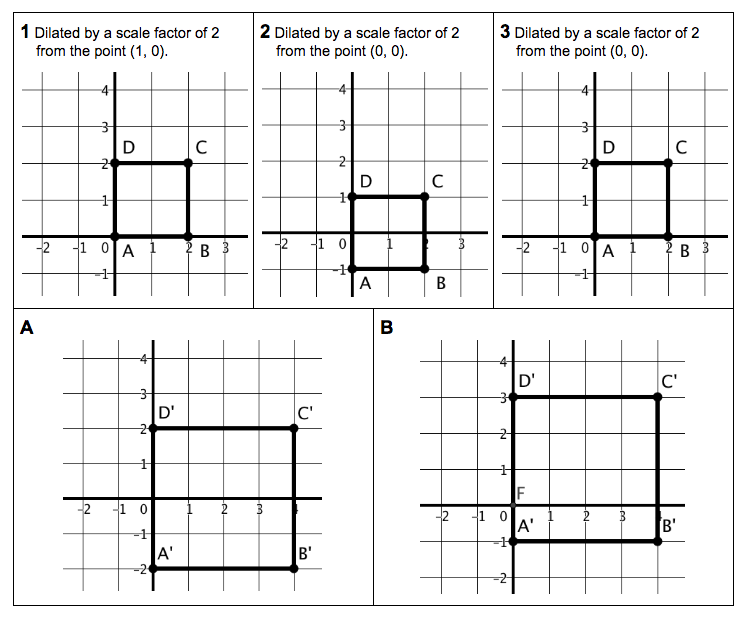
- transform polygons and describe the relationship between a pre-image and its image under a transformation on the coordinate plane
- apply and justify the ratio of the scale factor on perimeter and area
- apply and justify the ratio of the scale factor on perimeter and area
- prove geometric relationships on the coordinate plane
- prove two figures are congruent or similar in the coordinate plane
- use similarity relationships to determine ratios between segments
- classify a polygon using characteristics of its sides, angles, and diagonals
- determine what information is sufficient to prove the classification of a triangle/ quadrilateral
- given a specified polygon, find coordinates of points or lengths or directions of line segments that make the classification valid
- prove two figures are congruent or similar in the coordinate plane
Develop conceptual understanding:
perimeter, area
Supporting terms to communicate:
slope, distance, length, parallel, perpendicular, partition, dilation, equilateral, right, isosceles, quadrilateral, rectangle, square, rhombus, parallelogram, diagonals, bisect, midpoint, perpendicular bisector, height, base