Evidence of Understanding
- describe the relationship between angles formed by two intersecting lines
- use tools to explore and describe linear pairs and vertical angles
- Discuss the impacts of human error
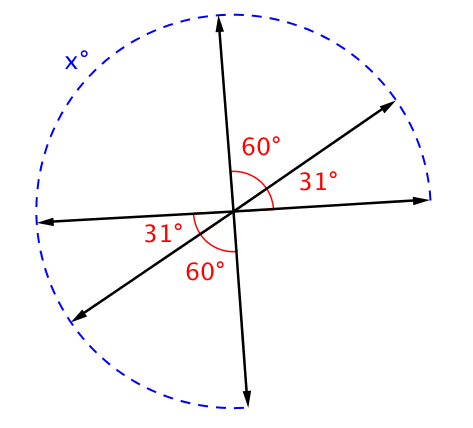
- justify, using transformations and constructions, that vertical angles are congruent
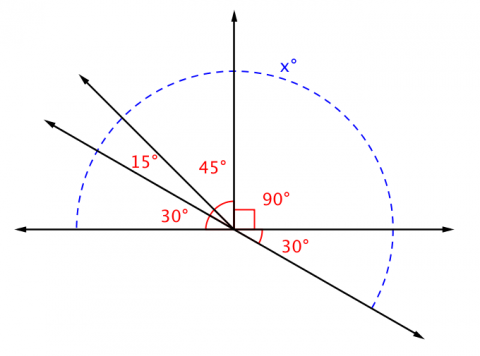
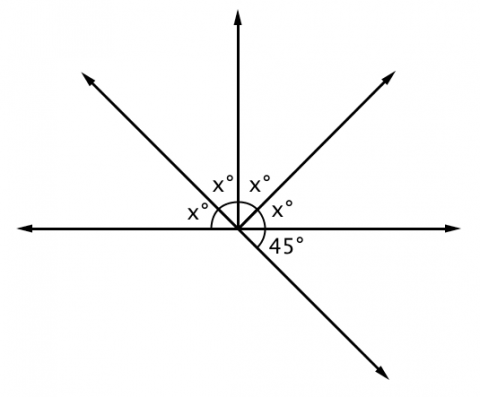
- use the angle addition postulate to show why supplementary angles sum to 180
- deductively prove vertical angles must be congruent using the reflexive and transitive properties
- explain and apply the subtraction property of equality (Euclid’s third common notion)
- find the measure of an angle using complementary, supplementary, or vertical pairs
- use tools to explore and describe linear pairs and vertical angles
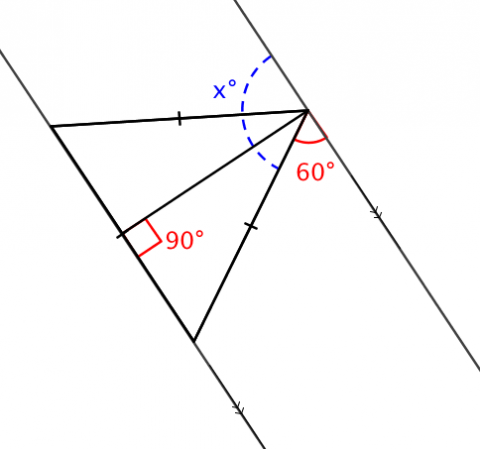
- explore angle relationships formed by a transversal and a pair of parallel lines
- use tools to make conjectures about parallel lines with a transversal
- use constructions and transformations (and other tools) to map angles to each other
- construct two congruent angles using a rigid motion transformation and parallel lines
- measuring many pairs of angles and generalizing findings to justify when two angles are congruent or supplementary
- prove that two lines are parallel using congruent angle relationships (the converse statement)
- apply properties of vertical angles and linear pairs to prove that two angles are congruent or supplementary
- create shared definitions for corresponding, alternate interior, alternate exterior, same-side interior or same-side exterior angles (also referred to as consecutive interior or consecutive exterior angles)
- find the measure of a missing angle
- use tools to make conjectures about parallel lines with a transversal
Develop conceptual understanding:
linear pair, supplementary, vertical angles, reflexive property, transitive property, complementary, parallel, transversal, corresponding, alternate interior, alternate exterior, same-side (or consecutive) interior angles, same-side (or consecutive) exterior anglesSupporting terms to communicate:
adjacent, opposite, perpendicular, bisect, degree measure, human error, sum, equal measure, congruent, construct, rotate, translate, reflect, map, carry onto