Evidence of Understanding
- distinguish trapezoids, parallelograms, rectangles, kites, rhombuses, and squares using properties of their sides and angles
- analyze examples and nonexamples to create and and test conjectures about quadrilaterals
- identify and use properties that result in quadrilaterals being part of the same “family”
- Examples: rectangle, square, and rhombus are all parallelograms, and all parallelograms are trapezoids
- Examples: rectangle, square, and rhombus are all parallelograms, and all parallelograms are trapezoids
- explore and prove relationships about interior and exterior angles of quadrilaterals and regular polygons
- apply knowledge about triangles to generate and test conjectures about quadrilaterals and other regular polygons
- use diagonals (auxiliary lines) to partition figures into triangles to determine the the sum of the interior angles of a polygon
- justify thatinterior angles of a quadrilateral always add up to 360° using examples and non-examples
- use tools to draw quadrilaterals, measure angles, and explain the impact of human error
- prove the interior angles for any quadrilateral sum to 360°
- find the value of missing interior and exterior angles in a polygon
- apply knowledge about triangles to generate and test conjectures about quadrilaterals and other regular polygons
- explore and prove relationships about angles and sides of a parallelogram
- identify and justify congruent angles and sides of a parallelogram
- make conjectures and use dynamic software, index cards, transparencies, paper folding, etc. to study sides and angles
- prove opposite sides and angles of a parallelogram are congruent
- apply properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal
- prove same side/consecutive interior angles of a parallelogram are supplementary
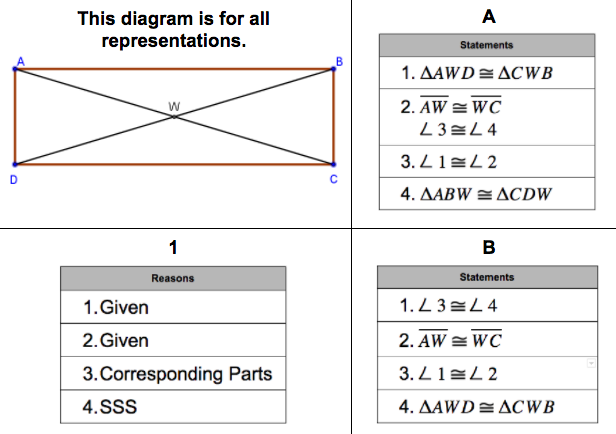
- prove a given figure is a square, rectangle, or rhombus
- apply properties of parallelograms, parallel lines, and triangle congruence criteria
- find the measure of a missing value or measurements
- identify and justify congruent angles and sides of a parallelogram
Develop conceptual understanding:
quadrilaterals, rectangle, square, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezoid, kite, diagonalSupporting terms to communicate:
example, non-example, human error, supplementary, bisect, perpendicular, parallel, transversal, auxiliary line, interior angles, adjacent side/angle, opposite side/angle, SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS, CPCTC