Evidence of Understanding
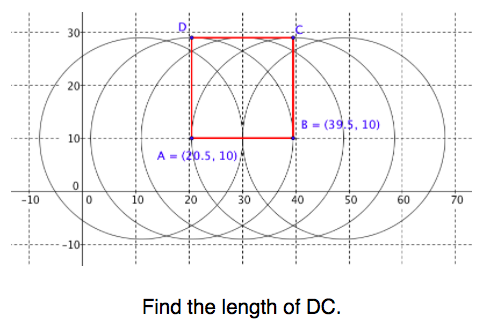
- describe qualities of polygons
- use examples and non-examples to justify a figure is a polygon
- distinguish irregular and regular polygons using congruent sides and congruent angles
- create and justify all of the lines of symmetry for a regular polygon (use paper folding, drawing, reflective devices, etc.)
- use isosceles triangles to understand qualities about regular polygons
- decompose regular polygons into congruent triangles
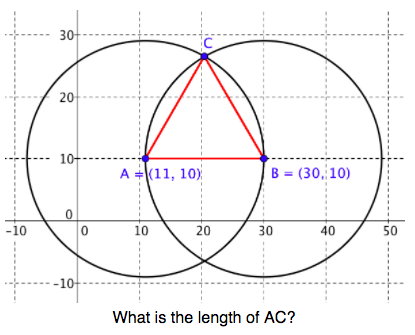
- use properties of circles to construct an equilateral triangle
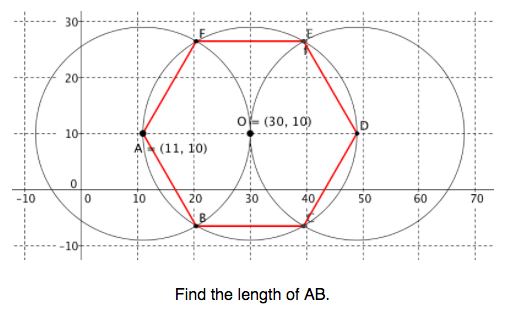
- use properties of circles to construct a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle
- explore congruent parts of regular polygons using lines of reflection and center of rotation
- demonstrate how rotational symmetry and line symmetry carry a polygon onto itself
- describe rotations as preserving congruence (isometry) and orientation
- use tools to justify that the line of symmetry, or line of reflection, is the perpendicular bisector
- construct the perpendicular bisector
- explain that the distance of each point of the figure from the line of reflection (line of symmetry) is the same
- generalize qualities about regular polygons using rotational and line symmetry
- Example: connect lines of symmetry with congruent parts within a polygon and the degree of rotation that carries a polygon onto itself
- specify the reflection or rotation that carries a polygon onto itself
- calculate the degree measures that can carry a polygon onto itself
- use the coordinate plane to write the equation of a horizontal or vertical line that carries a polygon onto itself
- demonstrate how rotational symmetry and line symmetry carry a polygon onto itself
Develop conceptual understanding:
polygon, regular polygon, irregular polygon, equilateral, inscribed, rotate, reflect, rotational symmetry, line symmetry, isometry, orientation, line of symmetry, line of reflection, perpendicular bisector
Supporting terms to communicate:
examples, non-examples, congruent, side, angle, triangle, square, pentagon, octagon, preserve, perpendicular, bisect, degree measure, clockwise, counterclockwise