- NV Math Team
- Getting Started
- Algebra I Archive
- 1: Curriculum Components
- 2: Instructional Routines
- 2A: Contemplate then Calculate
- 2B: Connecting Representations
- 2C: Group Learning Routines
- 2D: Additional Instructional Routines
- 3: ELL and SpEd Student Support
- A1 U0: Introduction to Algebra I
- A1 U1: Modeling with Functions
- A1 U2: Linear and Exponential Functions
- A1 U3: Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable
- A1 U4: Linear Equations and Inequalities in Two Variables
- A1 U5: Quadratic Functions
- A1 U6: Quadratic Equations
- A1 U7: Statistics
- Geometry & Algebra II Archive
- Geo U0: Introduction to Geometry
- Geo U1: Tools of Geometry
- Geo U2: Proofs about Congruence
- Geo U3: Similarity and Proof
- Geo U4: Right Triangle Trigonometry
- Geo U5: Extending to Three Dimensions
- Geo U6: Coordinate Geometry
- Geo U6: Circles
- A2 U0: Introduction to Algebra II
- A2 U1: Families of Functions
- A2 U2: Exponential Functions
- A2 U3: Trigonometric Functions
- A2 U4: Rational and Polynomial Functions
- A2 U5: Probability
- A2 U6: Statistics (Inferences from Data)
- Regents Readiness
- Find Resources
Find Resources
Search and browse resources for your classroom.
Use the filters below to see resources for a specific course, unit, and more.
- Common Core: Major Standards
- Common Core: Supporting Standards
- Common Core: Additional Standards
- Common Core: Practice Standards
Showing 47 Resources:
<style type="text/css"><!--td {border: 1px solid #ccc;}br {mso-data-placement:same-cell;}-->
</style>
This video provides an example of building intellectual need for students. Why do naming conventions matter? Because it's extremely difficult to talk about points with names for each of them.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry

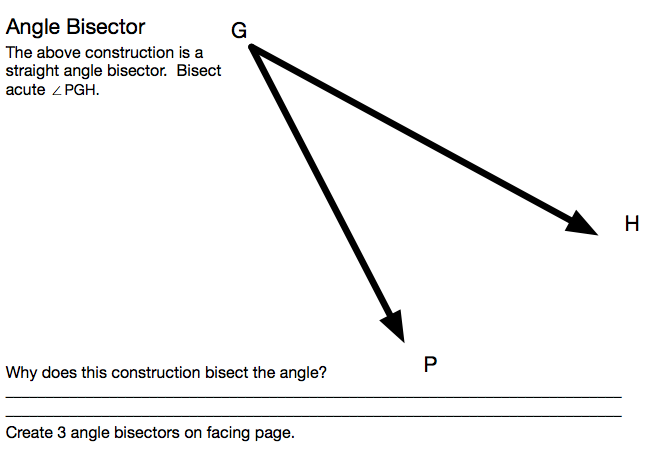
The last construction lesson in the series is for the Angle Bisector. I struggled with the scaffold to get students to make the first arc on the page. After they made the arc, the rest of the page was achievable by all. I was especially impressed with how easy it was to transition from the first construction to the second for students.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry
Geo U1: Tools of Geometry
<style type="text/css"><!--td {border: 1px solid #ccc;}br {mso-data-placement:same-cell;}-->
</style>
This task provides the most famous construction to bisect a given angle. It applies when the angle is not 180 degrees. Since the rays forming a 180 degree angle are collinear, this case can be handled separately by constructing the perpendicular to a line through a given point: note that the construction in the collinear case is actually the same as the one employed here except that the two circles in step (b) need to have radii larger than r so that they meet in two points.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry

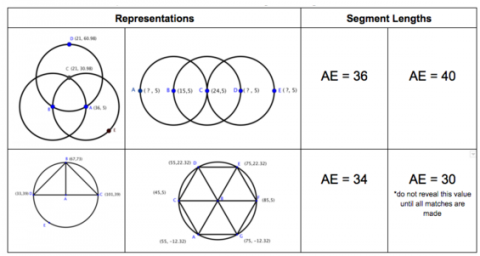
Use visual representations of circle diagrams to justify that congruent segments have equal measure.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry
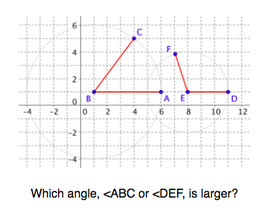
Use the structure of the grid to help learn how to compare angle size.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry
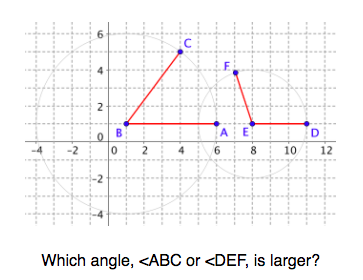
Use the structure of the grid to help learn how to compare angle size.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry

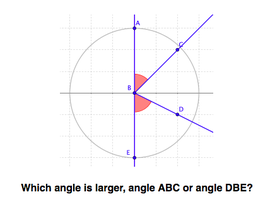
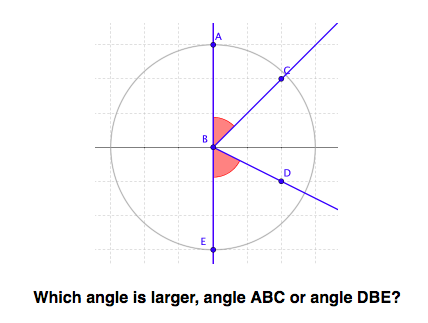
Use the structure of the grid and construction markers to learn how to compare angle size.
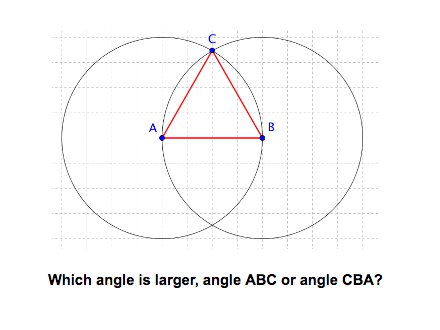
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry

Match constructions to representations of SSS, which then leads to showing the triangles are congruent to each other.

Experiment with transformations in the plane. Given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and reflections that carry it onto itself.
Clarification: Trapezoid is defined as “A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides.”
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Make geometric constructions. Construct an equilateral triangle, a square, and a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry

Match representations of angle constructions to resulting shapes by connecting to what students know about polygons or chunking both constructions and the polygons to focus on side-angle or side-side relationships.

Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry

Students will be able to identify the key points created by constructing 2 circles. Students will explore the relationship between the size of constructed circles, the distance between them, and the way that the segment between the centers is cut.

Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry

Students will explore the relationship between the size of constructed circles, the distance between them, and the type of triangle that can be created from the circles.

Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry

Continuing in a series of construction lessons, I created a worksheet for Copying an Angle and Parallel through a point. (an application of copying an angle.) Before this lesson, students need to understand that an angle is the measure of an arc between the two rays. Even with this information, the lesson needs scaffolds in place to get them to understand that it is the same radius arc and the length of that arc is the same as well.

Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
Experiment with transformations in the plane. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch).
Make geometric constructions. Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Clarification: Constructions include but are not limited to the listed constructions. Example: constructing the median of a triangle or constructing an isosceles triangle with given lengths.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
- Geo U1
Tools of Geometry